Cisco's CI/CD Pipeline Weaknesses:Hard-Coded Credentials & Misconfigurations Revealed

Introduction
In recent weeks, reports have surfaced regarding a significant breach involving Cisco, exposing sensitive data from various organizations. This blog post delves into the details of the breach, the compromised data, the implicated companies, and the methods used by attackers to gain access to such critical information.

Overview of the Breach
The breach, which dates back to June 10, 2024, has revealed a treasure trove of compromised data, including:
- GitHub Projects
- GitLab Projects
- SonarQube Projects
- Source Code
- Hard-Coded Credentials
- Certificates
- Customer Source Code Repositories (SRCs)
- Cisco Confidential Documents
- Jira Tickets
- API Tokens
- AWS Private Buckets
- Docker Builds
- Azure Storage Buckets
- Private and Public Keys
- SSL Certificates
- Cisco Premium Products
several major companies have reportedly had their production source codes taken, including Verizon, AT&T, and AT&T Mexico.
Evidence of the Breach: Screenshots and Samples
The samples confirm the leak of internal systems like Jenkins, and likely indicate that attackers had extensive access to Cisco's internal development tools, which allowed them to download source code and customer-related information. This breach may also compromise those customers, whose details are listed here, exposing them to targeted attacks or further exploitation.
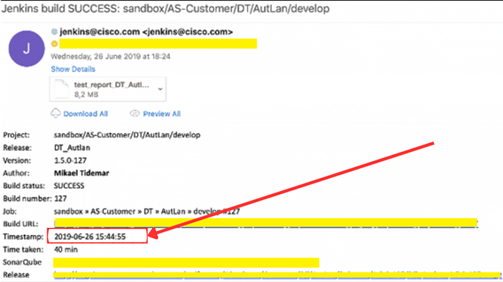
This breach appears to be an older compromise, likely originating from 2019 based on the Jenkins build timestamp and the outdated contract details. The attackers seem to have accessed Cisco’s CI/CD pipeline (Jenkins), likely through misconfigurations, credential theft, or exploiting vulnerabilities in the Jenkins environment or other integrated tools like SonarQube and cloud services. They may have had long-term access, exfiltrating sensitive data such as source codes, credentials, and customer contracts.
While the breach may have occurred years ago, the data has likely resurfaced recently on the dark web for sale, indicating the attackers are trying to profit from it now. This highlights the importance of securing internal systems and monitoring the dark web for leaked data, even long after an initial breach.
CI/CD Pipeline Vulnerabilities: Exposure of Source Code, Credentials, and Sensitive Data
The breach in Cisco's CI/CD pipeline exposed several critical vulnerabilities within their Jenkins system. One key issue was the exposure of sensitive GitHub repositories. The Jenkins configuration contained URLs to private repositories, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access, especially if credentials were compromised.
Another significant flaw was the presence of hard-coded credentials within the Jenkins files. These credentials, embedded in the configuration, could allow attackers direct access to repositories, cloud services, and internal systems, posing a serious security risk.

The use of Jenkins to deploy AWS resources revealed misconfigurations in cloud services. If AWS buckets and other cloud infrastructure were inadequately secured, attackers could access sensitive data, such as API tokens, customer information, and more.
Moreover, the Jenkins job management lacked essential security controls. The absence of proper encryption, access control, and secure job triggers made it easier for attackers to manipulate build jobs and access sensitive deployment details, such as SSL certificates and Docker builds.
Finally, the reuse of credentials across different services further weakened security. If the same credentials were reused across multiple systems, attackers could escalate their access, compromising more than just the initial system. This breach underscores the need for stronger CI/CD security practices, including multi-factor authentication and better credential management
.Possible Method Behind the Breach
The attackers likely exploited misconfigurations and vulnerabilities within Cisco's CI/CD pipeline, particularly targeting Jenkins. Analysis of a Jenkins configuration file reveals several critical points:
- Exposed GitHub Repository: The configuration includes URLs to private repositories, which, if compromised, could lead to unauthorized access to source code and sensitive project information.
- Credential Management: The presence of
fields indicates stored credentials used for authenticating with external services. Attackers could exploit these credentials to gain access to other systems or services. - Cloud Deployment Vulnerabilities: The usage of cloud deployment plugins, specifically for AWS, suggests that attackers could potentially access and manipulate cloud resources if they obtained these credentials.
- Long-Term Access: Given the age of some configurations (dating back to 2019), attackers may have established long-term access to the internal systems, allowing for sustained exfiltration of sensitive data.
The Dark Web Connection
As this information resurfaces on the dark web, it's evident that attackers are looking to profit from older breaches. This underscores the importance of organizations continuously monitoring for leaked data and ensuring their internal systems are secure.
Conclusion
The recent Cisco breach serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in CI/CD pipelines and the critical need for robust security practices. Organizations must prioritize securing their development environments, manage credentials diligently, and regularly audit configurations to prevent similar breaches. The resurfacing of such data on the dark web highlights the long-lasting implications of security breaches and the necessity for ongoing vigilance.
About Foresiet!
Foresiet is the pioneering force in digital security solutions, offering the first integrated Digital Risk Protection SaaS platform. With 24x7x365 dark web monitoring and proactive threat intelligence, Foresiet safeguards against data breaches and intellectual property theft. Our robust suite includes brand protection, takedown services, and supply chain assessment, enhancing your organization's defense mechanisms. Attack surface management is a key component of our approach, ensuring comprehensive protection across all vulnerable points. Compliance is assured through adherence to ISO27001, NIST, GDPR, PCI, SOX, HIPAA, SAMA, CITC, and Third Party regulations. Additionally, our advanced antiphishing shield provides unparalleled protection against malicious emails. Trust Foresiet to empower your organization to navigate the digital landscape securely and confidently.
Protect your brand, reputation, data, and systems with Foresiet's Integrated Digital Risk Platform. 24/7/365 threat monitoring for total peace of mind.


July 10, 2025, 9 a.m.
