HUNTUBS Ransomware Attack on Tata Technologies: A Major Cybersecurity Breach

Introduction
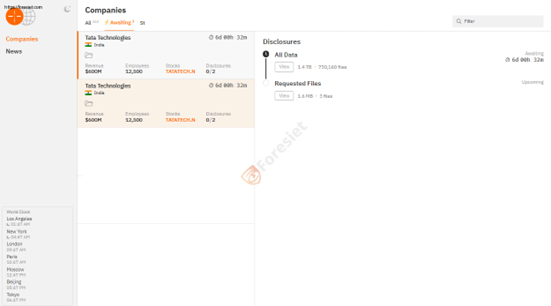
Cybersecurity incidents continue to make headlines, with the latest victim being Tata Technologies, a leading global engineering and technology services company. The HUNTUBS ransomware group has claimed responsibility for a major attack, leaking sensitive corporate data. The incident, which resulted in the theft of 1.4 TB of confidential data, has raised concerns about cybersecurity resilience among major enterprises.
About Tata Technologies
Tata Technologies Limited is a subsidiary of the Tata Group, specializing in engineering services, digital transformation, and product lifecycle management (PLM). With a reported revenue of $600 million, the company plays a critical role in industries like automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing. It is a trusted partner for major global enterprises, making it a high-value target for cybercriminals.
Timeline of the Attack
January 31, 2025 – Initial Disclosure
On January 31, 2025, Tata Technologies officially disclosed a cybersecurity incident in a letter to the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange of India (NSE). The company reported that:
- Certain IT assets were impacted by a ransomware attack.
- Some IT services were temporarily disrupted but later restored.
- Client delivery services remained unaffected.
- Cybersecurity experts were engaged to investigate the breach and mitigate its impact.
- Stated that they had exfiltrated 1.4 TB of sensitive data from Tata Technologies.
- Highlighted the company’s financial strength ($600 million revenue) and 12,500 employees.
- They threatened to leak the stolen data unless their ransom demands were met.
This disclosure was made in compliance with Regulation 30 of SEBI's Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements (LODR) Regulations, 2015, ensuring transparency with stakeholders.

March 4, 2025 – HUNTUBS Ransomware Group Takes Responsibility
On March 4, 2025, the HUNTUBS ransomware group publicly claimed responsibility for the attack. In a dark web post, they:
How did the Attack Happened?
Initial access in ransomware incidents often occurs through phishing emails, where attackers use malicious links or attachments to steal employee credentials. Another common vector is exploiting vulnerabilities in unpatched software, misconfigured VPNs, or weak Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) settings, allowing unauthorized entry. Additionally, attackers may leverage third-party compromises, targeting suppliers or partners with weaker security measures to infiltrate the primary organization's network.
Once inside the network, attackers engage in lateral movement and data exfiltration to maximize their impact. They often perform privilege escalation by leveraging tools like Mimikatz or LSASS dumps to obtain admin-level access. With elevated privileges, they deploy ransomware, encrypting critical files using strong encryption algorithms such as AES-256 and RSA-2048. Before encryption, attackers frequently exfiltrate sensitive data using tools like Rclone, MegaSync, or custom scripts, ensuring they have leverage for double extortion tactics.
After encrypting critical files and exfiltrating sensitive data, attackers initiate the ransom demand and extortion phase. They often employ the double extortion tactic, threatening to leak or sell stolen data if the victim refuses to pay. Ransom negotiations typically take place on dark web forums or encrypted chat platforms, where attackers demand payments in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Monero to maintain anonymity and evade tracking.
Tata Technologies’ Response
Since the attack, Tata Technologies has been actively collaborating with cybersecurity experts and law enforcement agencies to investigate and mitigate its impact. In response, the company has strengthened endpoint security and monitoring to detect and prevent future threats, implemented additional network segmentation and access controls to limit lateral movement, and reassured stakeholders of their commitment to data protection, ensuring transparency and reinforcing trust.
Final Thoughts
The HUNTUBS ransomware attack on Tata Technologies serves as a critical wake-up call for businesses worldwide. While our researchers are still validating the full scope of the incident, there are indications that the attackers may have leveraged new tactics or exploited an undisclosed CVE to gain access.
This highlights the urgent need for proactive cybersecurity measures, including regular security audits, patch management, and advanced endpoint detection & response (EDR) solutions to prevent such intrusions. The Zero Trust security model, which enforces strict access verification, can significantly reduce the risk of lateral movement. Additionally, employee security training remains essential to combat phishing attempts, a common initial access vector.
Lastly, a well-tested incident response plan, including robust backup and disaster recovery strategies, is crucial to minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. As investigations continue, organizations must stay vigilant, adaptive, and prepared for evolving ransomware threats.
About us!
Foresiet is the pioneering force in digital security solutions, offering the first integrated Digital Risk Protection SaaS platform. With 24x7x365 dark web monitoring and proactive threat intelligence, Foresiet safeguards against data breaches and intellectual property theft. Our robust suite includes brand protection, takedown services, and supply chain assessment, enhancing your organization's defense mechanisms. Attack surface management is a key component of our approach, ensuring comprehensive protection across all vulnerable points. Compliance is assured through adherence to ISO27001, NIST, GDPR, PCI, SOX, HIPAA, SAMA, CITC, and Third Party regulations. Additionally, our advanced antiphishing shield provides unparalleled protection against malicious emails. Trust Foresiet to empower your organization to navigate the digital landscape securely and confidently.
Protect your brand, reputation, data, and systems with Foresiet's Integrated Digital Risk Platform. 24/7/365 threat monitoring for total peace of mind.


