X-FILES Infostealer: Unraveling a Potent Threat to Global Cybersecurity

Introduction
In the dynamic world of cyber threats, the X-FILES stealer has emerged as a particularly dangerous and sophisticated piece of malware. First discovered in March 2021, this malware gained significant attention after a second variant surfaced later that year. Known for its efficiency in targeting vulnerable systems globally, X-FILES has become a top priority for cybersecurity professionals.
Origins and Evolution
The X-FILES stealer was first identified on a darknet forum in March 2021. Its origin traces back to phishing domains hosted on Russian IPs, with even its Command and Control (C2) panel being hosted on Russian infrastructure. This geographical linkage hints at a sophisticated threat actor, possibly state-sponsored or operating with tacit approval from local authorities.
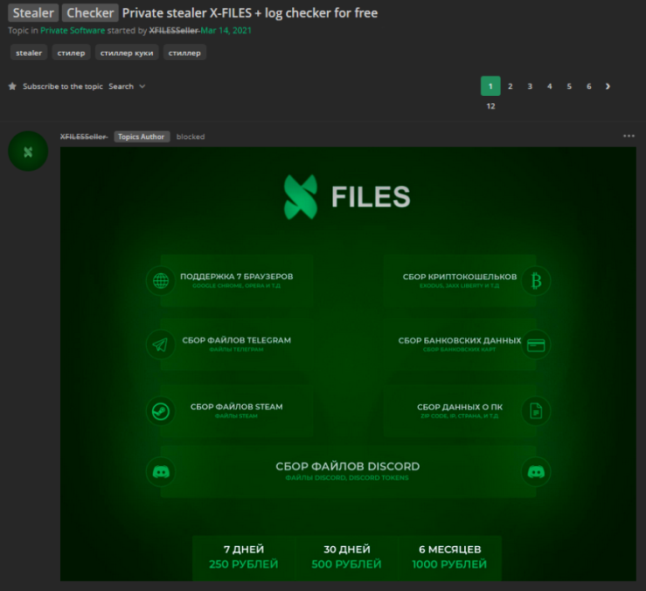
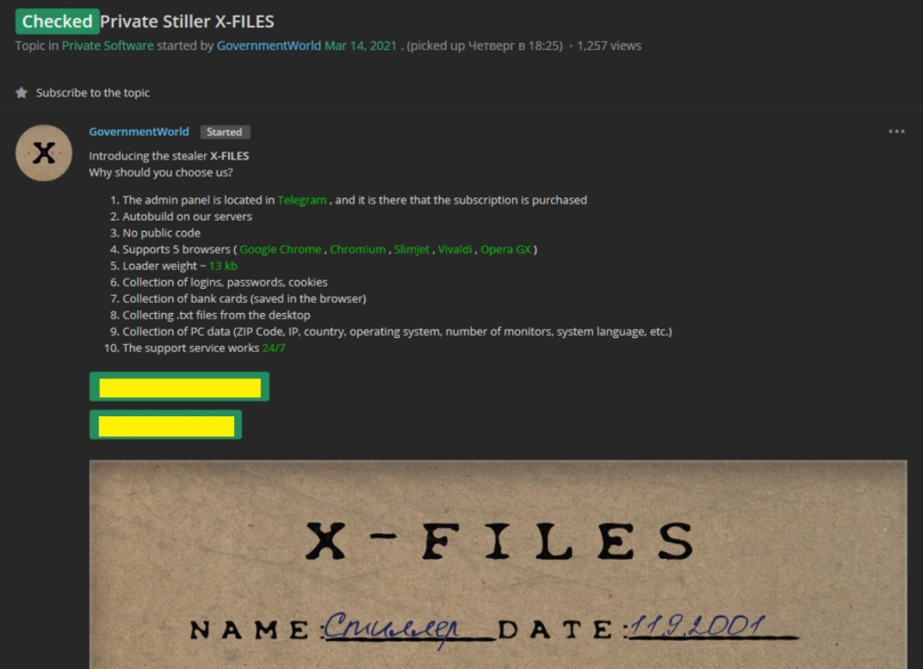
Posted on dakweb forum on March 2021
What is X-FILES Stealer?
X-FILES is a stealer malware written in the C programming language, designed to infiltrate machines running Windows 7 through Windows 11. It has been actively advertised on dark web forums, where cybercriminals exchange updates and training manuals on its deployment.

System Information collected by the latest variant
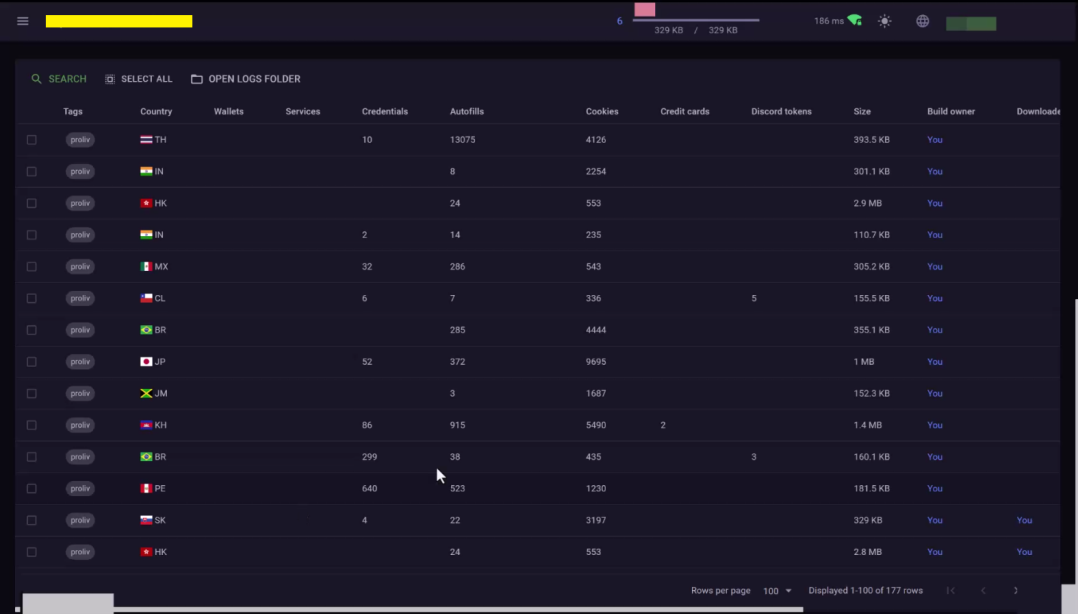
The primary objective of X-FILES is to exfiltrate sensitive information from infected systems, including browser data, cookies, passwords, autofill data, credit card information, and even cryptocurrency wallet details.
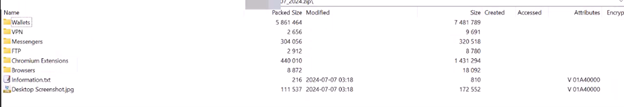
Stealer's working directory on the host
It includes a customizable logging system with detailed data on each log, notifications through Telegram, and automated updates to keep the tool current with the latest evasion techniques. Security features like GEO-blocking for CIS countries and regular stub cleaning ensure low detection rates, while upcoming features such as VNC configuration collection and automated password decryption signal continuous development, making it a potent threat for organizations.
Key Features and Capabilities and Builder
X-FILES stealer is known for its wide-reaching capabilities, which include support for a diverse array of browsers and over 80 browser-based crypto wallets. The stealer is equipped to collect data from various messengers, encrypt files using its own framework, and execute complex exfiltration processes. Additionally, X-FILES-specific training manuals are available, which further empower cybercriminals to exploit this malware to its full potential.
The files are stored locally in newly-created directories and eventually exfiltrated via Telegram, taking advantage of the anonymity in the communications platform.
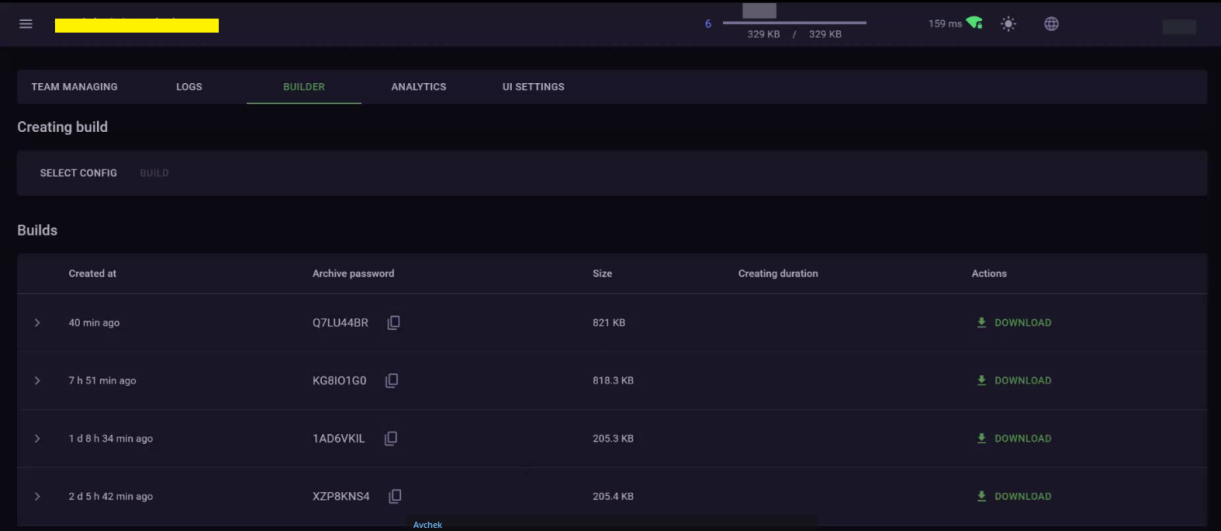
Builder image 1
Builder image 2
The malware operates stealthily, avoiding detection while collecting and transmitting critical information back to its operators. Its ability to run on a wide range of Windows versions makes it a versatile tool for cybercriminals.
Pricing and Support:
XFiles Stealer offers a subscription model priced at $200 per month. This subscription provides access to an extensive set of features, including a sophisticated control panel, team management functionalities, and customizable settings for log recording, notifications, and more. The pricing is designed to attract serious users who are looking for a premium stealer with high-level capabilities.
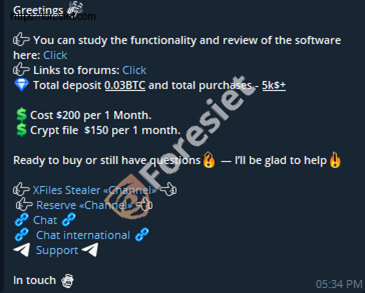
Screenshot shows Pricing and Support
Support Services:
The XFiles Stealer team provides 24/7 customer support through multiple channels, including Telegram, Jabber, TOX, and private messaging on the forum. The support team is highly responsive, assisting users with setup, configuration, and troubleshooting, ensuring smooth operation and satisfaction. Moreover, exclusive training manuals are provided, guiding users on how to profit from the stealer effectively. If a user is unable to achieve the desired results, a refund is offered, reflecting the team’s confidence in
XFiles Malware Enhances Delivery with Follina Exploit
XFiles info-stealing malware now supports Follina delivery, a vulnerability that was first discovered as a zero-day at the end of May and patched by Microsoft on June 14. The attack involves a malicious Word document received through spam email, which contains an OLE object linking to an HTML file with JavaScript code that exploits Follina.
This code retrieves a base64-encoded string with PowerShell commands to establish persistence in the Windows startup directory and execute the malware. The second-stage module, named “ChimLacUpdate.exe,” includes a hardcoded encrypted shellcode and AES decryption key, which is decrypted and executed within the same process. Following infection, XFiles performs typical info-stealer activities.
The resulting shellcode
This code is a typical example of how an attacker might load and execute shellcode within a process. The shellcode is first decrypted using an AES key, allocated in memory, and then executed using the ShellcodeDelegate.
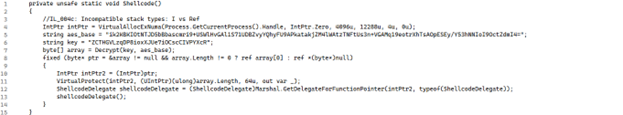
The resulting shellcode
This type of code is often found in malware, where the shellcode performs malicious activities such as spawning a reverse shell or downloading additional payloads.
AES Key and Base String & Decryption and Memory Handling
The provided code snippet is related to decrypting an AES-encrypted string using a specific key. The aes_base is a Base64-encoded string representing the encrypted data, while key is the string used as the decryption key. The decryption is performed by a Decrypt function, which returns a byte array containing the decrypted data.

Detailedof the shellcode
The code also includes memory handling with the fixed statement to pin the location of the byte array in memory, preventing the garbage collector from moving it during operations. This is particularly useful for low-level operations or when working with unmanaged code.
Command and Control Domains
The X-FILES stealer utilizes specific domains for its Command and Control (C2) operations. These domains are critical for the malware's operation, serving as the communication hub between the infected machines and the attackers. The following domains have been identified as part of the X-FILES infrastructure:
- bflow-musico[.]fun
- api-watch-films[.]space
These domains play a crucial role in maintaining the malware's functionality, allowing attackers to manage their operations remotely and execute commands on infected systems.
Telegram Integration and Support Channels
XFiles Reborn is an information stealer known for its robust support infrastructure, primarily operating through Telegram. The developers behind XFiles Reborn maintain several Telegram channels and bots to ensure seamless support and communication with their customers. The available channels include:
- News Channel: Regular updates and announcements related to XFiles Reborn.
- Updates Channel: Provides users with the latest updates and improvements to the stealer.
- Shopping Bot: An automated bot that facilitates the purchase of subscription plans.
- Direct Chat: A direct communication channel with the seller for any inquiries or issues.
- Customer Chat: A general chat for all customers to discuss and share experiences.
Subscription Plans XFiles Reborn offers flexible subscription plans tailored to different needs. The current pricing structure includes:
- 5 USD: Per week
- 10 USD: Per month
- 20 USD: For six months
These plans provide customers with access to the XFiles Reborn stealer, including support and updates.
XFiles Reborn Panel
The XFiles Reborn group strongly recommends using Telegram as the primary panel for gathering information from the stealers. This integration allows for easy access and management through the Telegram platform.

XFiles Reborn operation main page
However, for those who prefer a more traditional approach, XFiles Reborn also offers the option to create a “classic” panel on a Command and Control (C2) server provided by the seller. This flexibility ensures that users can choose the method that best suits their operational needs.
How to detect X-FILES?
To detect the X-FILES stealer, organizations should monitor for indicators of compromise (IOCs) such as unusual outbound traffic to known Command and Control (C2) domains, suspicious use of PowerShell commands, and the presence of encryption routines targeting browser and cryptocurrency wallet data. Additionally, keeping an eye on anomalous activity linked to phishing campaigns and using advanced threat detection tools to scan for the malware's specific hash values (MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256) can help identify infected systems before significant damage occurs.
Malware Families and ATT&CK Techniques
X-FILES stealer is associated with several malware families and employs various ATT&CK techniques to achieve its goals. The primary malware families include FILES, Regex, XmlReader, and Oldest.
These families contribute to the stealer's ability to collect and exfiltrate data while evading detection.
The malware also leverages multiple MITRE ATT&CK techniques, including:
- T1041 - Exfiltration Over C2 Channel: Exfiltrating data over a Command and Control (C2) channel to avoid detection.
- T1566 - Phishing: Leveraging phishing domains to initiate the infection process.
- T1027 - Obfuscated Files or Information: Using obfuscation techniques to hide malicious code.
- T1495 - Firmware Corruption: Potentially targeting firmware to ensure persistence or cause damage.
- T1003 - OS Credential Dumping: Extracting credentials stored in the operating system.
- T1005 - Data from Local System: Collecting data from the infected machine's local storage.
- T1018 - Remote System Discovery: Identifying remote systems within the network for further exploitation.
- T1047 - Windows Management Instrumentation: Utilizing WMI for malicious purposes.
- T1082 - System Information Discovery: Gathering detailed information about the infected system.
- T1083 - File and Directory Discovery: Exploring the file system to identify valuable information.
- T1140 - Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information: Reversing obfuscation to reveal critical data.
- T1189 - Drive-by Compromise: Exploiting vulnerabilities in browsers or plugins to gain access to the system.
- T1518 - Software Discovery: Identifying software installed on the system to tailor the attack.
- T1552 - Unsecured Credentials: Harvesting credentials stored insecurely on the system.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
To help detect and mitigate the threat posed by X-FILES stealer, security teams should be on the lookout for the following Indicators of Compromise (IOCs):
- MD5: b2474e803fa38f4e0ef97b4d3022371c
- SHA-1: 9f61926a398825afb4ce1b43c1f9677660248356
- SHA-256: df035dbf1a32469699c8c8b3c04b49ab8aad5ced1e874a1c21b918e1c606d797
These IOCs are critical for identifying systems that may have been compromised by the X-FILES stealer and should be integrated into your organization's threat detection mechanisms.
Expanding Threat Landscape
- Target Profiles: Identify the primary targets of X-FILES attacks, such as individuals, businesses, or specific industries. Understanding the target profile can help organizations tailor their security measures accordingly.
- Financial Impact: Quantify the potential financial losses associated with X-FILES infections, including stolen funds, identity theft, and business disruption. This can help stakeholders prioritize security investments.
- Emerging Threats: Discuss potential future developments of the X-FILES stealer, such as new features, delivery methods, or evasion techniques. Staying ahead of the threat landscape is crucial for effective defense.
Enhancing Prevention and Mitigation
- Best Practices: Provide actionable recommendations for individuals and organizations to prevent X-FILES infections, including email security, software updates, and user education.
- Incident Response: Outline steps to take in case of a X-FILES infection, such as isolating the affected system, containing the threat, and recovering data.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Emphasize the importance of sharing threat intelligence information with the cybersecurity community to collectively combat X-FILES and similar threats.
Additional Considerations
- Visualizations: Incorporate diagrams, flowcharts, or infographics to illustrate the malware's lifecycle, attack chain, or technical details. This can improve readability and understanding.
- Case Studies:b> Share real-world examples of X-FILES attacks to demonstrate the malware's impact and highlight successful mitigation strategies.
- Attribution: Discuss the challenges and potential implications of attributing X-FILES attacks to specific threat actors or nation-states.
By incorporating these suggestions, you can create an even more informative and valuable resource for understanding and combating the X-FILES stealer.
Conclusion
The X-FILES stealer is a formidable threat that continues to evolve, posing significant risks to organizations and individuals alike. As it targets sensitive information such as browser credentials, crypto wallets, FTP credentials, and credit card data, it is essential for security professionals to stay vigilant and implement robust security measures to protect against this malware.
At Foresiet Researchers, we are committed to staying ahead of emerging threats like X-FILES. Our team of experts continuously monitors the dark web and other threat vectors to provide our clients with the intelligence they need to safeguard their digital assets.
About Foresiet!
Foresiet is the pioneering force in digital security solutions, offering the first integrated Digital Risk Protection SaaS platform. With 24x7x365 dark web monitoring and proactive threat intelligence, Foresiet safeguards against data breaches and intellectual property theft. Our robust suite includes brand protection, takedown services, and supply chain assessment, enhancing your organization's defense mechanisms. Attack surface management is a key component of our approach, ensuring comprehensive protection across all vulnerable points. Compliance is assured through adherence to ISO27001, NIST, GDPR, PCI, SOX, HIPAA, SAMA, CITC, and Third Party regulations. Additionally, our advanced antiphishing shield provides unparalleled protection against malicious emails. Trust Foresiet to empower your organization to navigate the digital landscape securely and confidently.
Protect your brand, reputation, data, and systems with Foresiet's Integrated Digital Risk Platform. 24/7/365 threat monitoring for total peace of mind.


July 10, 2025, 9 a.m.
