Inside Anubis Ransomware: Tactics, Impact & Protection

Introduction
Recently, a new ransomware group, Anubis, has emerged, making its presence known on Twitter. The Foresiet Threat Intel team monitored their activity and observed a new ransomware operation being advertised on their account. The group updated their profile picture and began posting about their latest breaches.
Through analysis of their communication patterns and language, Foresiet has determined that the operators behind Anubis likely belong to a Russian-speaking threat group.
Their tactics, targeting methods, and underground forum activity further suggest their affiliation with Eastern European cybercriminal networks.
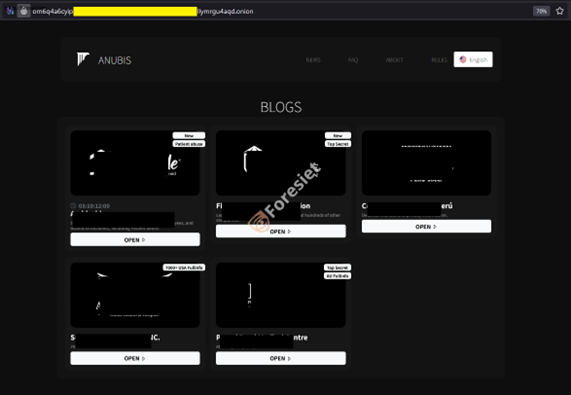
Anubis ransomware's leak site displaying victim listings and blog updates.

Their public-facing account used for announcements and victim shaming
Threat actors behind Anubis are leveraging various techniques to infiltrate systems, encrypt files, and demand ransom payments. Their operations extend beyond traditional ransomware attacks, incorporating elements of data extortion, underground market affiliations, and advanced evasion tactics.
This blog provides an in-depth analysis of Anubis ransomware, including its affiliates, attack methodologies, infrastructure, and recommendations for mitigation.
The Evolution of Anubis Ransomware
Anubis ransomware first surfaced publicly in December 2024, with the group announcing its activities on Twitter. Their first post highlighted a data breach involving a well-known company, signaling their intent to expose stolen data unless a ransom was paid.
Key features of Anubis ransomware include:
- Strong Encryption: Uses AES/RSA encryption to lock files, rendering them inaccessible without the decryption key.
- Data Exfiltration: Before encryption, sensitive data is stolen to be used for extortion.
- Ransom Note Delivery: Victims receive a file with ransom instructions, including contact details.
- Active Dark Web Presence: The group maintains multiple underground forum profiles, facilitating negotiations and recruitment.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Allows affiliates to distribute the malware in exchange for a share of the ransom.

The ransom message left on infected systems with payment instructions.
Anubis Ransomware: Affiliates and Operations
Anubis operates under a RaaS model, meaning multiple affiliates deploy ransomware. These affiliates gain access to the ransomware builder and infrastructure, enabling them to launch attacks in exchange for a percentage of the ransom payments.
Affiliates and Their Role
- Initial Access Brokers (IABs): Sell access to compromised networks through phishing, RDP vulnerabilities, or malware.
- Exploit Developers: Provide tools for spreading ransomware, including vulnerabilities and custom loaders.
- Money Launderers: Convert cryptocurrency ransom payments into fiat currency through mixing services.
- Negotiators: Handle ransom demands, communicating with victims via email or underground forums.
Observed Anubis Campaigns and Current Impact
As of March 24, 2025, Anubis ransomware has been linked to at least five known victims, with more potentially undisclosed cases. The group's dark web profiles indicate active recruitment and negotiations with potential partners.
Emergence and Operations
Formation and Activity: Anubis emerged in late 2024, with indications of activity as early as November 2024. The group's presence has been observed on forums like RAMP and XSS, where they operate under aliases such as 'superSonic' and 'Anubis__media'.
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Anubis functions as a RaaS operation, offering affiliates multiple monetization models, including traditional ransomware deployment, data extortion, and access monetization programs. This versatility has attracted a diverse range of cybercriminals to their affiliate network.
Tactics and Techniques
Double Extortion: The group employs double extortion tactics, encrypting victims' data and threatening to publicly release sensitive information if ransom demands are not met. This strategy increases pressure on victims to comply.
Recent Developments
February 2025 Surge: February 2025 witnessed a sharp rise in ransomware incidents, with 956 reported victims globally, marking an 87% increase from January. While groups like Clop and Play led this surge, new actors like Anubis contributed to the escalating threat landscape.
Technical Sophistication: Analyses of Anubis's malware reveal advanced obfuscation and encryption techniques. For instance, their Python-based backdoor employs multi-stage decryption processes, utilizing AES encryption and Base64 encoding to evade detection and complicate forensic analysis.
Targeted Industries and Regions
Critical Industries: Anubis has been observed targeting critical industrial sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. Their focus on these industries suggests an intent to disrupt essential services and extract significant ransoms.
Global Reach: The group's operations have a global footprint, with reported victims in the United States, Peru, and Australia. Notably, First Defense Fire Protection, a U.S.-based company, confirmed a data breach linked to Anubis.
Key Observations from Dark Web Forums
Anubis maintains an active presence on underground forums, operating under the alias "Anubis_media."
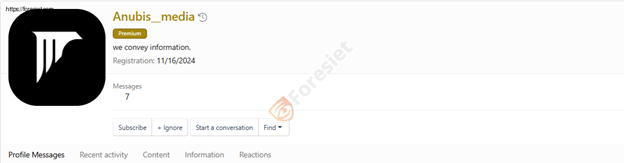
Their account on a hacking forum for selling data and recruiting affiliates.
Their activities include:
- Trading Stolen Data: Posts frequently reference "Fullz," a term indicating full personal data sets from various countries.
- Selling Corporate Access: Advertisements for "corporate access monetization 50/50" suggest involvement in brokering access to compromised networks.
- Sharing Medical Records: A post details "about 7300 fullinfo US medical clinic clients" containing sensitive information such as DOB, SSN, addresses, and phone numbers.
- Engagement with Buyers: Posts mention sending "material" to other users via private messages, reinforcing active data distribution.
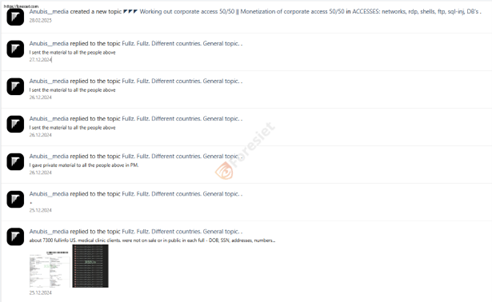
Conversations showing their interactions with victims and partners.
The forum activity ranges from December 2024 to February 2025, aligning with their public emergence.
Dark Web Profile FAQ: Extortion & Data Monetization
Anubis has provided a public FAQ on their dark web profile, outlining their extortion tactics and business practices:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
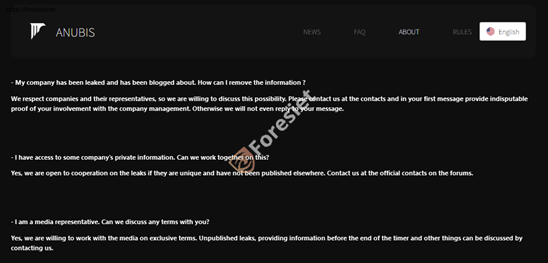
Their guidelines on negotiations, data leaks, and media interactions.
Q1: My company has been leaked and has been blogged about. How can I remove the information?
A1: We respect companies and their representatives, so we are willing to discuss this possibility. Please contact us at the contacts and in your first message provide indisputable proof of your involvement with the company management. Otherwise, we will not even reply to your message.
Q2: I have access to some company's private information. Can we work together on this?
A2: Yes, we are open to cooperation on the leaks if they are unique and have not been published elsewhere. Contact us at the official contacts on the forums.
Q3: I am a media representative. Can we discuss any terms with you?
A3: Yes, we are willing to work with the media on exclusive terms. Unpublished leaks, providing information before the end of the timer and other things can be discussed by contacting us.
This FAQ suggests Anubis not only engages in ransomware operations but also facilitates data monetization and cooperation with third parties, including media entities and insiders.
Email Addresses Used for Ransom Demands:
- anubis@mailum.com
- anubis20@firemail.de
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
Anubis ransomware follows a multi-stage attack chain to maximize impact and extortion. The initial infection occurs through phishing emails containing malicious attachments, such as ZIP, RAR, or macro-enabled documents, and exploits Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) vulnerabilities for brute-force attacks. Additionally, attackers distribute the malware via trojanized software and fake updates.
Once inside the system, Anubis escalates privileges and moves laterally using PowerShell scripts and scheduled tasks to execute payloads while disabling security tools and deleting shadow copies to prevent recovery. The ransomware then encrypts files with a unique key per victim and exfiltrates sensitive data before encryption to strengthen their leverage.
During the extortion phase, ransom notes instruct victims to contact threat actors via email, such as anubis@mailum(.)com or anubis20@firemail(.)de where they claim to be open to negotiating the removal of victim data from their leak site.
Mitigation & Detection Strategies
For Organizations:
To protect against ransomware threats like Anubis, organizations should deploy advanced threat detection solutions such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or Extended Detection and Response (XDR) to identify and mitigate ransomware behaviors in real time. Regularly patching vulnerabilities is crucial to prevent cybercriminals from exploiting outdated software and security flaws. Enforcing the principle of least privilege by restricting administrative access helps minimize the potential damage in case of an attack.
Additionally, continuous network traffic monitoring can detect suspicious communication with malicious IPs or domains, allowing for early intervention. Lastly, maintaining secure offline backups ensures that critical data remains protected and can be restored in the event of ransomware encryption, reducing the impact of an attack.
For Individuals:
To enhance cybersecurity and reduce the risk of ransomware attacks, it is essential to avoid suspicious emails by refraining from opening unknown attachments or clicking on suspicious links, as these are common attack vectors.
Keeping software updated by regularly applying security patches helps close vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection against credential theft, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Additionally, installing reputable security software, such as antivirus programs, provides real-time protection against malware and other cyber threats, further strengthening an organization's security posture.
Conclusion
Anubis ransomware represents a dangerous evolution of modern cyber threats. With its growing infrastructure, dark web presence, and expanding list of victims, organizations must remain vigilant against this persistent threat. The ransomware’s ability to encrypt files, steal sensitive data, and extort victims through multiple channels makes it a formidable adversary.
By implementing strong cybersecurity practices, continuously monitoring threat intelligence, and enforcing proactive defense strategies, individuals and organizations can mitigate the risks posed by Anubis ransomware. Staying informed about the latest developments in ransomware operations is essential to staying one step ahead of cybercriminals.
For further updates, regularly check threat intelligence feeds and cybersecurity research sources. If you suspect an Anubis ransomware infection, report the incident to the relevant cybersecurity authorities immediately.
About us!
Foresiet is the pioneering force in digital security solutions, offering the first integrated Digital Risk Protection SaaS platform. With 24x7x365 dark web monitoring and proactive threat intelligence, Foresiet safeguards against data breaches and intellectual property theft. Our robust suite includes brand protection, takedown services, and supply chain assessment, enhancing your organization's defense mechanisms. Attack surface management is a key component of our approach, ensuring comprehensive protection across all vulnerable points. Compliance is assured through adherence to ISO27001, NIST, GDPR, PCI, SOX, HIPAA, SAMA, CITC, and Third Party regulations. Additionally, our advanced antiphishing shield provides unparalleled protection against malicious emails. Trust Foresiet to empower your organization to navigate the digital landscape securely and confidently.
Protect your brand, reputation, data, and systems with Foresiet's Integrated Digital Risk Platform. 24/7/365 threat monitoring for total peace of mind.


July 1, 2025, 7:17 p.m.

July 1, 2025, 7:07 p.m.