Hellcat Ransomware: A Growing Threat to Businesses and Organizations

Introduction:
Hellcat ransomware emerged in early November 2024 and quickly became a notable threat in the cybersecurity landscape. The group first gained attention on November 6, 2024, when it claimed responsibility for a cyberattack against Schneider Electric. Known for its aggressive tactics and unique ransom demands, Hellcat is already making its mark in the world of ransomware. Despite its recent appearance, the group's actions have raised alarms due to their persistent targeting of high-profile organizations and their reputation for data theft and extortion.

Initially operating under the name International Contract Agency (ICA), the group rebranded as Hellcat after concerns about the name’s associations with terrorism. This shift was strategic, as the new name reflected their bold and fearsome approach. As the group continues its activities, its methods and tactics make it a significant threat to organizations worldwide.
Key Characteristics of Hellcat Ransomware:
- Aggressive Tactics:
- Hellcat is known for its highly aggressive approach, not only encrypting files but also threatening to release stolen data unless ransom demands are met. This makes them especially dangerous, as they amplify the pressure on victims to comply.
- Frequent Targeting of Large Organizations:
- The group has consistently targeted major organizations like Schneider Electric, marking their third attack on the company in 18 months. This suggests that Hellcat is focused on high-profile victims with potentially sensitive and valuable data.
- Rebranding for Strategic Identity:
- Initially operating under the name International Contract Agency (ICA), the group rebranded to Hellcat to distance itself from potential associations with terrorism. This new identity aligns with their fearsome, aggressive persona and may have been part of a broader strategy to instill fear in their victims.
- Data Theft and Blackmail:
- Hellcat's primary tactic involves stealing sensitive data and threatening to release it unless a ransom is paid. Their demands often involve the exfiltration of large amounts of data, with threats to expose over 40 GB in their most recent attack.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities:
- The group has been reported to exploit specific vulnerabilities in platforms like Atlassian Jira, through which they accessed Schneider Electric’s systems. This highlights their focus on targeting misconfigured or unpatched software in organizational infrastructures.
- Publicly Vowed Threats:
- Hellcat has been vocal in its demands, frequently publicizing its threats and showcasing stolen data. This public approach is designed to heighten pressure on victims, making them more likely to negotiate or pay the ransom.
- Credential-based Entry:
- Like many ransomware groups, Hellcat likely relies on compromised credentials, often obtained through phishing or weak password policies, to gain initial access to targeted systems.
Recent Attacks
Schneider Electric Breach:
On November 4, 2024, Hellcat executed one of its most high-profile attacks, breaching Schneider Electric's systems. The ransomware group claimed to have accessed and exfiltrated sensitive data, with threats to release over 40 GB of stolen information unless their ransom demands are met.
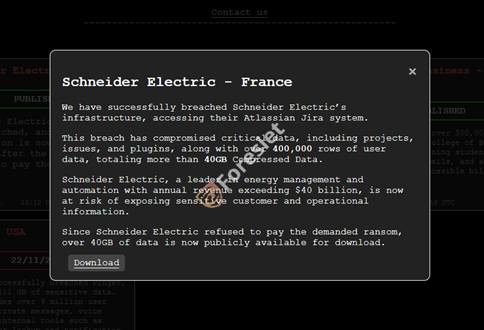
Pattern of Targeting:
This marks the third ransomware attack on Schneider Electric within 18 months, following incidents involving the Cactus ransomware and Cl0p ransomware group. The repeated targeting highlights potential vulnerabilities in Schneider Electric’s cybersecurity defenses and the strategic persistence of threat actors like Hellcat.
Ongoing Threats
Hellcat’s strategy revolves around high-pressure tactics:
- Data Leaks: Public threats to expose stolen data amplify the stakes, potentially leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
- Public Statements: Their vocal announcements about breaches and demands fuel their infamy, encouraging a fear-driven response from victims.
Exploited Vulnerabilities
Atlassian Jira Entry Point:
Reports suggest Hellcat exploited vulnerabilities in Schneider Electric's Atlassian Jira environment to gain unauthorized access. This emphasizes the critical need for organizations to secure their cloud-based tools and configurations.
Historical Exploits:
In previous attacks, Schneider Electric fell victim to:
- The MOVEit zero-day vulnerability, leveraged by Cl0p ransomware.
- Weaknesses exploited by the Cactus ransomware group.
These incidents underline the importance of proactive vulnerability management and continuous monitoring.
General Ransomware Tactics
Hellcat’s modus operandi aligns with broader ransomware trends:
- Credential Compromise: Threat actors often use stolen or weak credentials, frequently obtained through phishing campaigns.
- Unpatched Software: Exploiting outdated software remains a primary attack vector, emphasizing the need for timely security updates and patching.
Mitigation and Defense
Organizations must adopt a proactive cybersecurity posture to mitigate the risks posed by ransomware groups like Hellcat. Key steps include:
- Regular Patch Management: Ensure all software and systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Strengthening Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and robust password policies to minimize credential-based breaches.
- Incident Response Preparedness: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to quickly detect, isolate, and respond to ransomware attacks.
- Comprehensive Backup Strategy: Maintain secure, offline backups to mitigate the impact of data encryption or loss during an attack.
Conclusion
The rise of Hellcat ransomware highlights the evolving threat landscape in the cybersecurity domain. Their audacious attacks serve as a wake-up call for organizations to prioritize cybersecurity measures, strengthen defenses, and remain vigilant against emerging threats.
As the Hellcat ransomware group continues its operations, a proactive and resilient approach is essential to thwart their efforts and safeguard critical systems and data.
About us!
Foresiet is the pioneering force in digital security solutions, offering the first integrated Digital Risk Protection SaaS platform. With 24x7x365 dark web monitoring and proactive threat intelligence, Foresiet safeguards against data breaches and intellectual property theft. Our robust suite includes brand protection, takedown services, and supply chain assessment, enhancing your organization's defense mechanisms. Attack surface management is a key component of our approach, ensuring comprehensive protection across all vulnerable points. Compliance is assured through adherence to ISO27001, NIST, GDPR, PCI, SOX, HIPAA, SAMA, CITC, and Third Party regulations. Additionally, our advanced antiphishing shield provides unparalleled protection against malicious emails. Trust Foresiet to empower your organization to navigate the digital landscape securely and confidently.
Protect your brand, reputation, data, and systems with Foresiet's Integrated Digital Risk Platform. 24/7/365 threat monitoring for total peace of mind.


Nov. 29, 2024, 5:43 p.m.